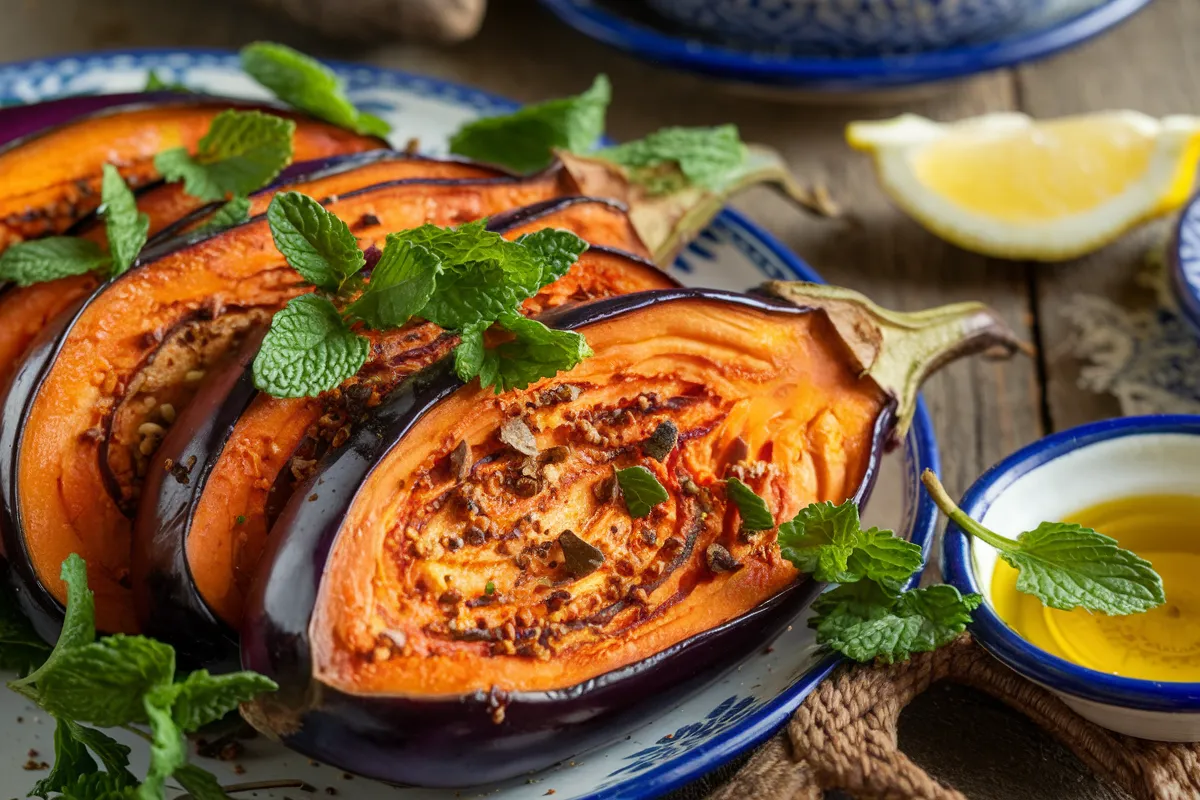
Have you ever wondered, “What does Turkish eggplant taste like?” If so, you’re in the right place. Turkish eggplant, especially the Turkish Orange Eggplant, is known for its sweet and mild flavor. This article explores the unique taste of Turkish eggplant, how it compares to other types, the best ways to prepare it, and its nutritional benefits.
Introduction to Turkish Eggplant
So, what does Turkish eggplant taste like compared to other eggplants? Turkish eggplant is a smaller, round variety that changes color from green to vibrant orange as it ripens. This type of eggplant is a staple in Turkish cuisine, where it has been used for centuries. Unlike the more common purple eggplant, Turkish Orange Eggplant is valued for its sweetness and mild flavor, making it versatile in many dishes.
Turkish Eggplant in Traditional Dishes
In Turkish markets and kitchens, this eggplant is appreciated for both its flavor and cultural significance. It often appears in traditional dishes like imam bayildi and karniyarik, serving as both a main ingredient and a tasty side. As more people explore global cuisines, chefs and home cooks are discovering the unique qualities of Turkish eggplant. Whether you roast, grill, or stuff it, Turkish eggplant offers a taste that is both familiar and distinct.
If you’re ready to try a more complex dish, consider making Turkish Stuffed Eggplant. This recipe highlights the versatility of Turkish eggplant by combining its creamy texture with various fillings.
What Does Turkish Eggplant Taste Like?
The Flavor Profile
So, what does Turkish eggplant taste like when it comes to sweetness and texture? Turkish eggplant has a mild, vegetal flavor with a natural sweetness. This sweetness is more noticeable when the eggplant is harvested before it fully ripens, giving it a delicate taste compared to other eggplants.
Cooking and Flavor Enhancement
When cooked, Turkish eggplant becomes creamy, making it an ideal ingredient in many dishes. Its mild flavor allows it to blend well with other ingredients. This makes it a great base for a variety of meals. For more insights on the sweetness of different eggplants, including Turkish Orange Eggplant, check out this article by NPR. Understanding how sweetness varies across eggplant types can help you choose the best one for your recipes.
Key Flavor Characteristics
- Sweetness: The sweet taste of Turkish eggplant stands out, especially when harvested at the right time. This sweetness makes it a favorite in both traditional and modern dishes. It pairs well with savory and spicy flavors, making it a versatile choice.
- Mildness: Turkish eggplant has a subtle flavor that blends well with many ingredients. Its mildness allows it to absorb the flavors of spices, herbs, and other components in a dish.
- Bitterness: While Turkish eggplant can be slightly bitter when underdeveloped, this is easy to manage. Proper cooking techniques, such as roasting or grilling, reduce bitterness. To further reduce any bitterness, try soaking the eggplant in milk before cooking. This method ensures a smooth and consistent taste.
The combination of sweetness and mildness makes Turkish eggplant a versatile ingredient for various dishes. Whether you’re preparing a simple side or a complex main course, the flavor profile of Turkish eggplant will enhance your culinary creations.
Texture Profile
- Raw Texture: Turkish eggplant is firm and less spongy when raw. This makes it a good choice for salads if prepared properly. Its firm texture also makes it easier to slice and handle in the kitchen, which is useful when making dishes that need the eggplant to hold its shape, like stuffed or grilled eggplant.
- Cooked Texture: Once cooked, Turkish eggplant becomes creamy and soft, with a tender flesh that melts in your mouth. The contrast between the creamy flesh and slightly firmer skin adds a delightful texture to dishes. This creaminess is one of the reasons why Turkish eggplant is so popular in dips, spreads, and purees.
Understanding how Turkish eggplant’s texture changes with different cooking methods can help you get the best results in your recipes.
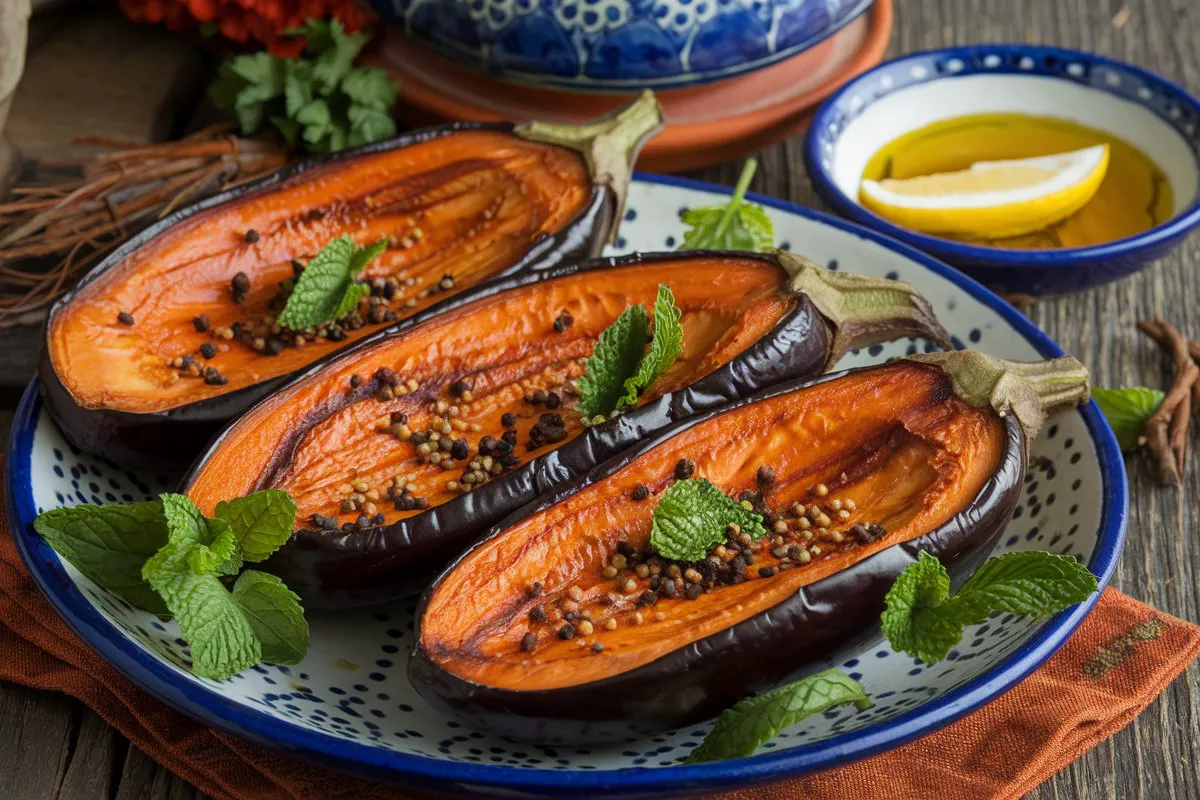

Culinary Uses and Cooking Methods
Preparing Turkish Eggplant
What does Turkish eggplant taste like when cooked? Turkish eggplant is versatile and can be prepared in many ways. Its mild and sweet flavor makes it a perfect ingredient for a wide range of dishes, from appetizers to main courses.
Popular Cooking Methods
- Roasting: Roasting enhances the sweet and smoky flavors of Turkish eggplant, making it ideal for spreads like baba ganoush or as a side dish. The high heat of roasting caramelizes the sugars in the eggplant, intensifying its sweetness and adding depth to its flavor.
- Roasting tips: To get the best results when roasting Turkish eggplant, slice it into even pieces, drizzle with olive oil, and season with salt and pepper. Roast in a preheated oven at 400°F (200°C) for 25-30 minutes, or until the eggplant is golden brown and tender. For extra flavor, add garlic, herbs, or spices to the roasting pan.
- Grilling: Grilling adds a slight char to the eggplant, enhancing its sweet and mild flavor. This method works well for salads or as a main course. The smoky notes from the grill add a delicious contrast to the eggplant’s natural sweetness.
- Grilling tips: When grilling Turkish eggplant, slice it into thick rounds or lengthwise strips. Brush with olive oil and season with salt and pepper. Grill over medium-high heat for 3-4 minutes per side, or until grill marks appear and the eggplant is tender. Grilled Turkish eggplant pairs beautifully with fresh herbs, tangy cheeses, and vibrant sauces.
- Sautéing: Sautéing helps retain the firmness of the eggplant while softening the interior, making it ideal for stir-fries or as a pizza topping. The quick cooking time of sautéing allows the eggplant to keep its shape and texture while absorbing the flavors of the other ingredients.
- Sautéing tips: To sauté Turkish eggplant, cut it into bite-sized pieces and heat a tablespoon of olive oil in a large skillet over medium heat. Add the eggplant and cook for 5-7 minutes, stirring occasionally, until the eggplant is golden brown and tender. Sautéed Turkish eggplant works well in various dishes, from pasta to rice bowls.
For another delicious way to enjoy eggplant, try stuffed eggplant recipes. These recipes combine rich fillings with the tender, creamy flesh of Turkish eggplant, showcasing its versatility.
Best Pairings and Ingredients
- Herbs: Fresh herbs like basil, parsley, and mint complement the mild flavor of Turkish eggplant. These herbs add a burst of freshness to dishes, enhancing the eggplant’s natural sweetness while providing a bright and aromatic contrast.
- Herb pairing tips: Basil works well with grilled or roasted Turkish eggplant, while parsley adds a fresh note to sautéed or baked dishes. Mint can be used to add a refreshing touch to eggplant salads or as a garnish for eggplant-based dips and spreads.
- Spices: Spices like cumin, coriander, and smoked paprika add depth to the sweet and mild taste of the eggplant. These spices bring warmth and complexity to dishes, making Turkish eggplant a great base for bold, robust flavors.
- Spice pairing tips: Cumin and coriander work well in Middle Eastern and Mediterranean dishes, complementing the eggplant’s sweetness and enhancing its savory notes. Smoked paprika adds a subtle smokiness that pairs beautifully with roasted or grilled Turkish eggplant.
- Oils and Acids: Olive oil and lemon juice or vinegar balance the flavors and enhance the eggplant’s natural sweetness. The richness of olive oil adds a luscious texture, while the acidity of lemon juice or vinegar brightens the dish and cuts through the richness.
- Oil and acid pairing tips: Use extra virgin olive oil for its fruity, robust flavor, and combine it with freshly squeezed lemon juice or a splash of balsamic vinegar to add a tangy contrast. These combinations work well in salads, marinades, and dressings.
Nutritional Benefits and Health Aspects
So, what does Turkish eggplant taste like? It’s not just flavorful—it’s also nutritious. Turkish eggplant is low in calories but rich in essential vitamins and minerals, making it a healthy addition to any diet. Whether you’re looking to boost your intake of antioxidants, improve heart health, or simply enjoy a delicious vegetable, Turkish eggplant has much to offer.
Nutritional Profile
Turkish eggplant is a nutrient-dense food that offers various health benefits. It is high in Vitamin C, Vitamin A, and dietary fiber, all of which are crucial for overall health. Its low-calorie content makes it a great choice for those looking to maintain a healthy weight or reduce calorie intake.
- Vitamins and Minerals: Turkish eggplant is rich in vitamins and minerals like Vitamin C, Vitamin A, potassium, and folate. These nutrients play essential roles in supporting immune function, maintaining healthy skin, and promoting heart health.
- Vitamin C: This antioxidant is important for immune health and helps protect the body from oxidative stress. It also plays a role in collagen production, which is vital for healthy skin, joints, and connective tissues.
- Vitamin A: Essential for vision and immune function, Vitamin A also helps maintain healthy skin and mucous membranes.
- Potassium: This mineral helps regulate blood pressure and supports muscle and nerve function.
- Folate: Folate is important for DNA synthesis and repair and plays a crucial role in fetal development during pregnancy.
- Dietary Fiber: Turkish eggplant is a good source of dietary fiber, which is important for digestive health. Fiber helps regulate bowel movements, prevent constipation, and may reduce the risk of certain digestive disorders, such as diverticulitis and colorectal cancer.
Health Benefits
The nutritional profile of Turkish eggplant translates into several health benefits. Adding this vegetable to your diet can support overall health and well-being.
- Antioxidants: The vibrant color of Turkish eggplant indicates a high level of antioxidants, which help protect the body from oxidative stress and inflammation. Antioxidants play a key role in neutralizing harmful free radicals, reducing the risk of chronic diseases like heart disease and cancer.
- Anthocyanins: These antioxidants, found in the skin of eggplants, have been shown to reduce inflammation and improve heart health. They may also help protect against certain cancers by inhibiting the growth of cancer cells.
- Nasunin: Nasunin, an anthocyanin in eggplant skin, protects cell membranes from damage. It also has anti-inflammatory properties and may help reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
- Heart Health: The low-calorie content and high fiber make Turkish eggplant a heart-healthy food. It is suitable for those looking to manage their weight or improve cardiovascular health. The potassium in eggplant also supports heart health by helping regulate blood pressure.
- Cholesterol Management: The fiber in Turkish eggplant may help lower cholesterol levels by binding to cholesterol in the digestive system and preventing its absorption into the bloodstream.
- Blood Pressure Regulation: Potassium helps counteract the effects of sodium, promoting healthy blood pressure levels. A diet rich in potassium-containing foods like Turkish eggplant can help reduce the risk of hypertension and heart disease.
For more health benefits, explore the health benefits of stuffed eggplant. Stuffed eggplant dishes are not only tasty but also provide a variety of nutrients that support overall health and well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What does Turkish eggplant taste like?
Turkish eggplant has a sweet and mild flavor with a creamy texture when cooked. This makes it distinct from other eggplant varieties. The combination of sweetness and creaminess makes it versatile for use in various dishes, from appetizers to main courses.
How do you cook Turkish eggplant to avoid bitterness?
To avoid bitterness, cook Turkish eggplant thoroughly using methods like roasting or grilling. These methods help mellow out any bitter notes. Additionally, soaking eggplant in milk before cooking can help reduce bitterness and enhance the eggplant’s natural sweetness.
Can you eat Turkish eggplant raw?
Yes, but it’s generally firmer and more bitter than when cooked, so it’s often better suited for cooking. If using raw Turkish eggplant in salads, slice it thinly and season it well to minimize bitterness and enhance its natural flavor.
What are the differences between Turkish eggplant and regular eggplant?
Turkish eggplant is smaller, often orange or red, and sweeter than the larger, purple varieties commonly found. The texture of Turkish eggplant is also creamier when cooked, making it a popular choice for dishes that require a smooth, rich consistency.
Where can you buy Turkish eggplant?
Turkish eggplant can be found in specialty markets, farmers’ markets, and sometimes in the international section of large grocery stores. It’s usually available in late summer and early fall when eggplants are in season.
Conclusion
So, what does Turkish eggplant taste like? It’s a unique and flavorful addition to any kitchen. Its sweetness, mildness, and creamy texture when cooked make it a versatile ingredient in a wide range of dishes. Whether you roast, grill, or sauté it, this eggplant variety will elevate your meals with its delightful taste.
For those looking to try a recipe that highlights Turkish eggplant, consider making a delicious Turkish Eggplant Salsa. This dish showcases its creamy texture and mild flavor in a fresh, vibrant way.
Incorporating Turkish eggplant into your diet not only enhances the taste of your meals but also provides numerous health benefits. From supporting heart health to offering essential vitamins and minerals, Turkish eggplant is a nutritious and delicious choice. Whether you’re an experienced cook or just starting, experimenting with Turkish eggplant can open up a world of culinary possibilities.